Pain
What is the Difference Between Pseudogout and Gout?
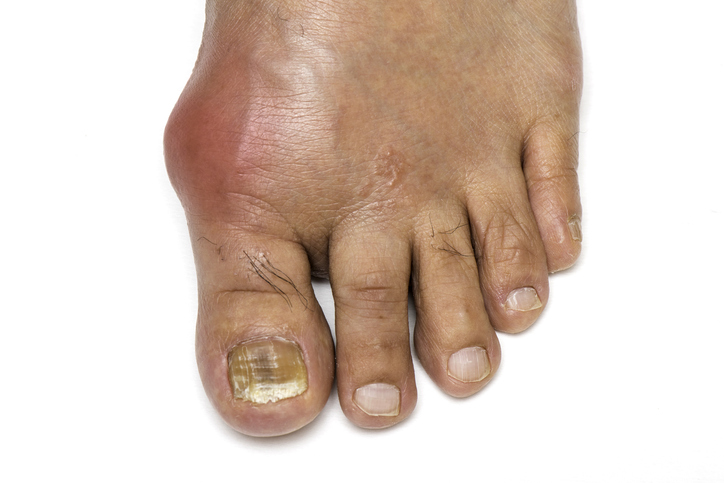
Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD) is also known as pseudogout or “fake gout” because of its similarities to gout. However, the conditions have several differences, including their symptoms, causes and treatments.
Symptoms
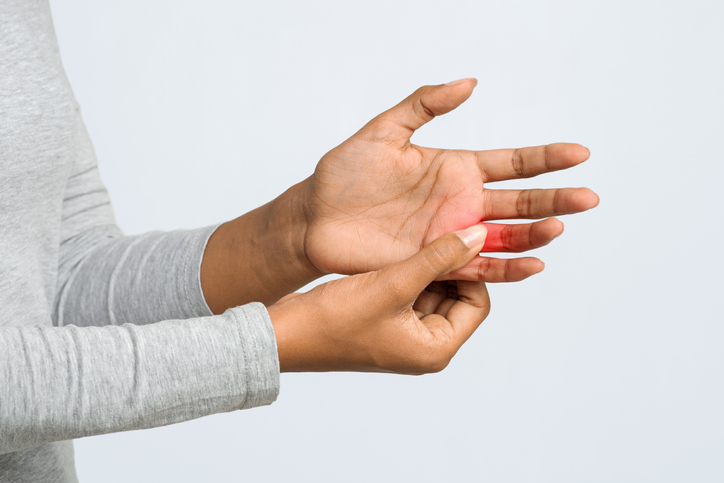
Both pseudogout and gout cause joint pain, swelling, redness and warmth. With gout, these symptoms most often affect the big toe, but with pseudogout, they typically affect a larger joint, such as the knee, wrist, or ankle.
While the symptoms for both conditions start abruptly, the symptoms of gout typically worsen for up to 12 hours then begin to reduce, going away after 7 to 10 days. The symptoms of pseudogout typically stay the same and last for days or weeks.
Causes
Although gout and pseudogout are both caused by crystal deposits in the cartilage and fluid in a joint, the types of crystals are different. Gout is caused by monosodium urate monohydrate crystals. Pseudogout is caused by calcium pyrophosphate crystals. For gout, the accumulation of crystals in a joint is caused by high levels of uric acid in the body, which can be identified on a blood test. The cause of the accumulation crystals in a joint with pseudogout is unknown. In rare cases, pseudogout and gout can occur at the same time.
Diagnosis
If joint fluid is taken from an affected joint (joint fluid aspiration), a microscope can be used to identify which type of crystals are present in the joint. Gout crystals are needle-shaped; whereas, pseudogout crystals are shaped more like rectangles.
Treatments
The two conditions share some common treatments, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids. However, gout can also be treated with medications and dietary changes that lower the levels of uric acid in the blood. The same is not true for pseudogout.
Although pseudogout and gout have many similarities, their differences allow physicians to properly diagnose and treat both conditions.