Pain
Conventional Medical Treatments for Gout

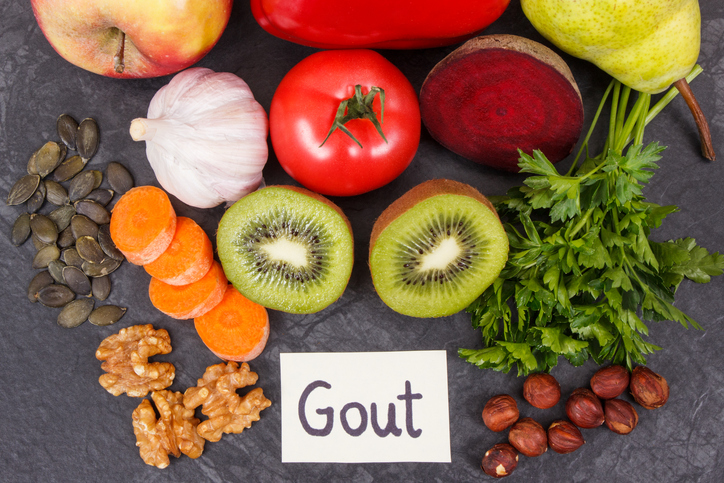
What is gout?
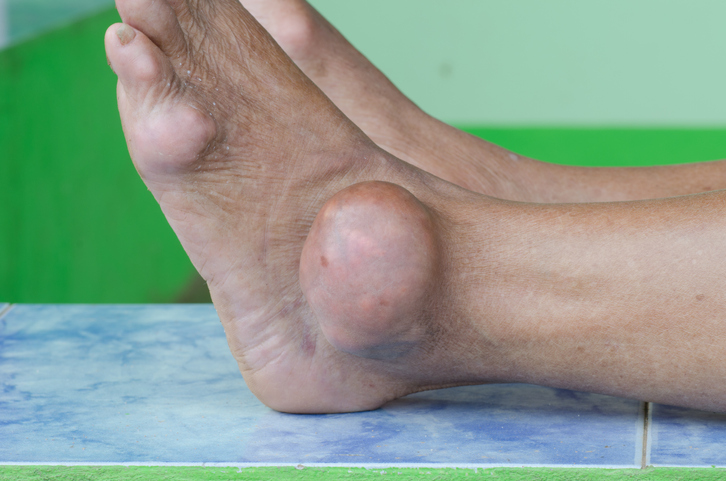
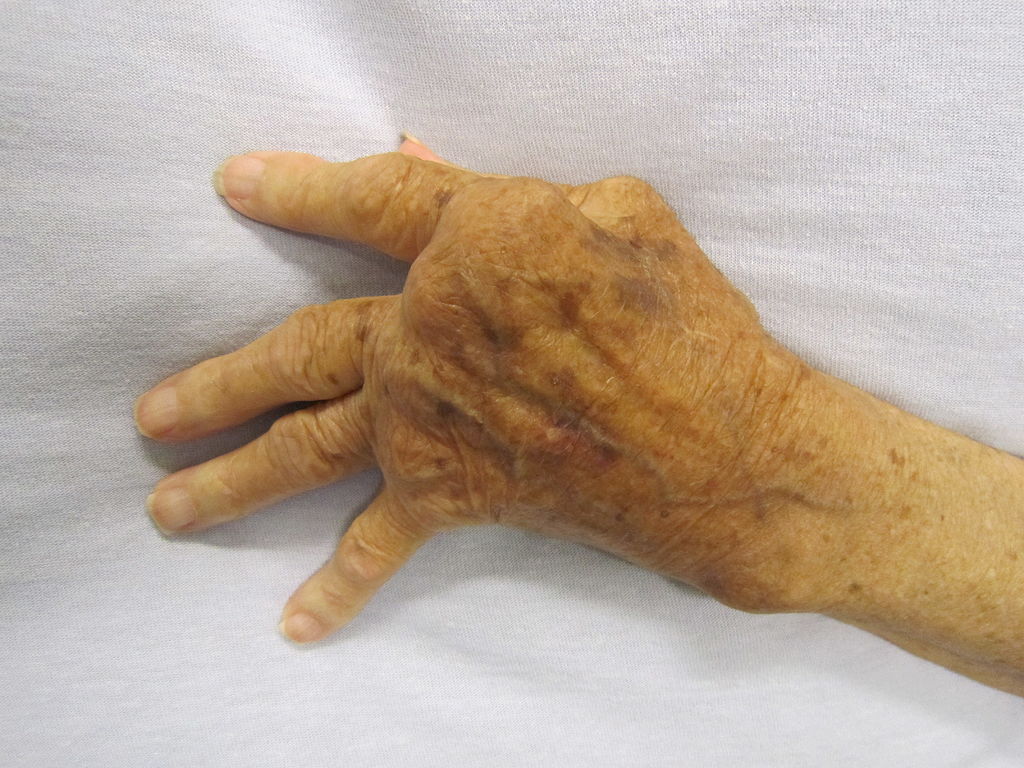
Gout is a complex form of arthritis that can develop when the blood contains high levels of uric acid. If the body produces too much uric acid or the kidneys excrete too little uric acid, it can build up in the blood and form sharp urate crystals in or around specific joints, most commonly the joint at the base of the big toe.
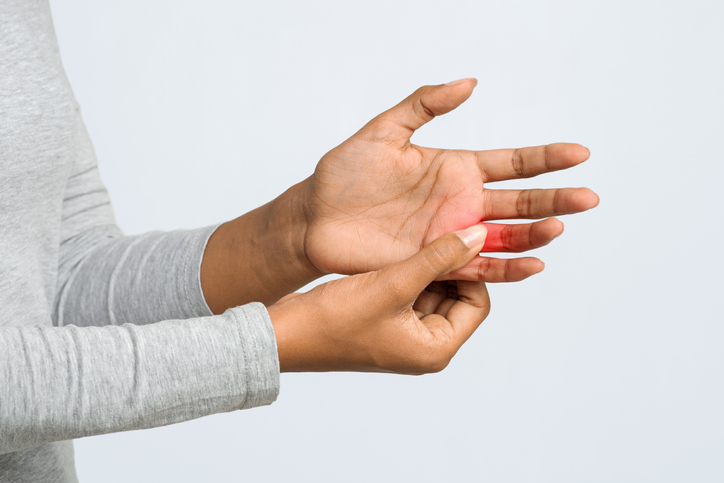
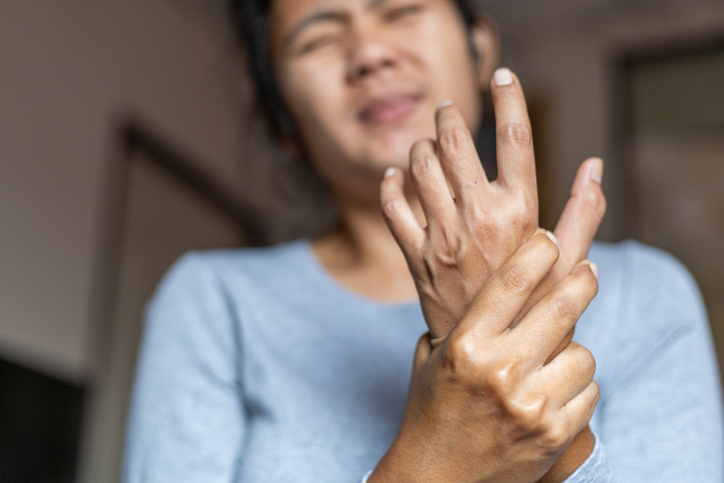
Gout attacks often occur suddenly and cause intense pain. The affected joint becomes hot, swollen, red, and extremely tender to the touch. A sensation that the joint is “on fire” is common, and even the weight of a sheet on the affected joint is extremely painful. Acute gout attacks typically last 3-10 days. Symptoms are not present between gout attacks. However, if left untreated, gout can become chronic and cause permanent damage to the affected joints.
Conventional medical treatments
Treatment of gout typically involves medication that either relieves pain and reduces inflammation or prevents future attacks. Medications used to treat gout include the following:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such over-the-counter (ibuprofen or naproxen) or prescription (indomethacin or celecoxib) medications, help with the inflammation associated with gout.
- Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, help control the inflammation and pain associated with gout.
- Colchicine may be prescribed to treat the pain and inflammation of a current gout attack or to prevent future gout attacks.
Medications prescribed to reduce uric acid levels, which helps to prevent future gout attacks, include:
- Xanthine oxidase inhibitors, such as allopurinol and febuxostat, lower the blood’s uric acid level and help reduce the risk of gout.
- Uricosurics, such as probenecid and lesinurad, improve the kidneys’ ability to remove uric acid from the body.
- Pegloticase is a medication that may be prescribed when standard medication options for reducing uric acid levels do not work. It works quickly and can lower uric acid faster than other medications. It involves IV therapy every two weeks.