Treatments
What Is Diclofenac Topical?

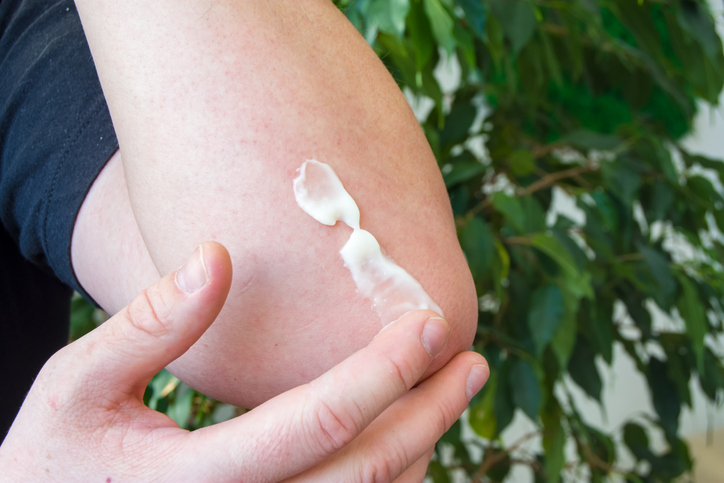
Diclofenac topical is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) most commonly used to help relieve joint pain in the knees, ankles, feet, hands, wrists and elbows. It is currently available both over-the-counter and by prescription. It works by reducing substances in the body that cause pain and inflammation.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved prescription diclofenac topical in 2007 as a non-opioid treatment option for osteoarthritis joint pain. It was approved by the FDA for over-the-counter use as of February 14, 2020.
The FDA deems diclofenac topical safe if used as directed; however, some experts consider diclofenac very risky. Diclofenac is considered one of the seven riskiest NSAIDs due to the increased risk of heart failure, especially if it is used in high doses.
Important warnings
Warning labels should be read prior to using diclofenac topical gel. Consulting a pharmacist or health care professional with any questions about diclofenac topical gel is recommended.
- A severe allergic reaction may occur, especially in individuals who are allergic to aspirin.
- Liver damage is possible if used with other products containing diclofenac or if used more often or longer than directed.
- Diclofenac increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and heart failure.
- Diclofenac may take up to seven days before relief is provided. Individuals are urged to stop use and seek medical attention if pain has not improved in seven days or if the need for use exceeds 21 days.
- Stomach or intestinal bleeding can occur with the use of diclofenac.
- Diclofenac topical is not approved for use for those under the age of 18.
- Diclofenac may affect ovulation, affecting fertility.
- Use of diclofenac may harm an unborn baby if used in the last three months of pregnancy.
- Diclofenac may not be safe to use while breastfeeding.
Proper use of diclofenac topical gel
- Diclofenac topical gel should only be used as directed and at the lowest effective dosage.
- This medication should only be used on the skin.
- If diclofenac gets in the mouth or eyes, it should be immediately rinsed out with water.
- Diclofenac topical should never be applied to areas of the skin with infections, rash, peeling, burns, or open wounds.
- Diclofenac should be stored at room temperature and away from moisture and heat.
- Two doses of diclofenac topical gel should never be applied at the same time. If a dose is missed, it should be applied as soon as possible; however, if it’s almost time for the next dose, the missed dose should be skipped.
Things to avoid while using diclofenac topical gel
- Avoid alcohol as it may increase the risk of stomach bleeding.
- Avoid exposing the treated area of skin to heat, tanning beds, and sunlight. Heat increases the amount of diclofenac absorbed through the skin.
- Avoid the use of sunscreen, lotions, medicated skin products, insect repellent, and cosmetics on the same area treated with diclofenac topical.
- Avoid getting diclofenac topical in the eyes; however, if this occurs, rinse well with water and call a health care professional if irritation lasts longer than one hour.
- Speak to a pharmacist or health care professional before using other medications to treat pain, fever, cold/flu, or swelling.
Diclofenac topical side effects
Common side effects of diclofenac topical include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Increased blood pressure
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Headache, drowsiness or dizziness
- Heartburn, nausea, vomiting, gas, or stomach pain
- Stuffy nose
- Stinging or burning in the eyes
- Itching or increased sweating
- Pain or swelling in the arms or legs
Stop using diclofenac and contact a health care professional if any of these side effects occur:
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling or rapid weight gain
- Skin rash
- Severe skin reaction
- Difficulty seeing
- High blood pressure
- Bloody or tarry stool, coughing up blood, or vomiting
- Liver problems
- Anemia
*Emergency medical attention should be sought if symptoms of an allergic reaction develop, such as hives, wheezing, breathing difficulty, facial or throat swelling, sneezing, or a runny or stuffy nose. Allergic skin reactions include fever, burning eyes, skin pain, sore throat, skin rash, or blistering and peeling of the skin.
Possible drug interactions
Certain antidepressant medications taken with any NSAID may cause the body to bruise or bleed more easily. Furthermore, prior to using diclofenac topical gel, a health care professional should be consulted if any of the following medications are currently being taken:
- Lithium
- Methotrexate
- Cyclosporine
- Heart or blood pressure medications
- Steroid medications
- Blood thinners