Pain
What Is Adjacent Segment Disease?

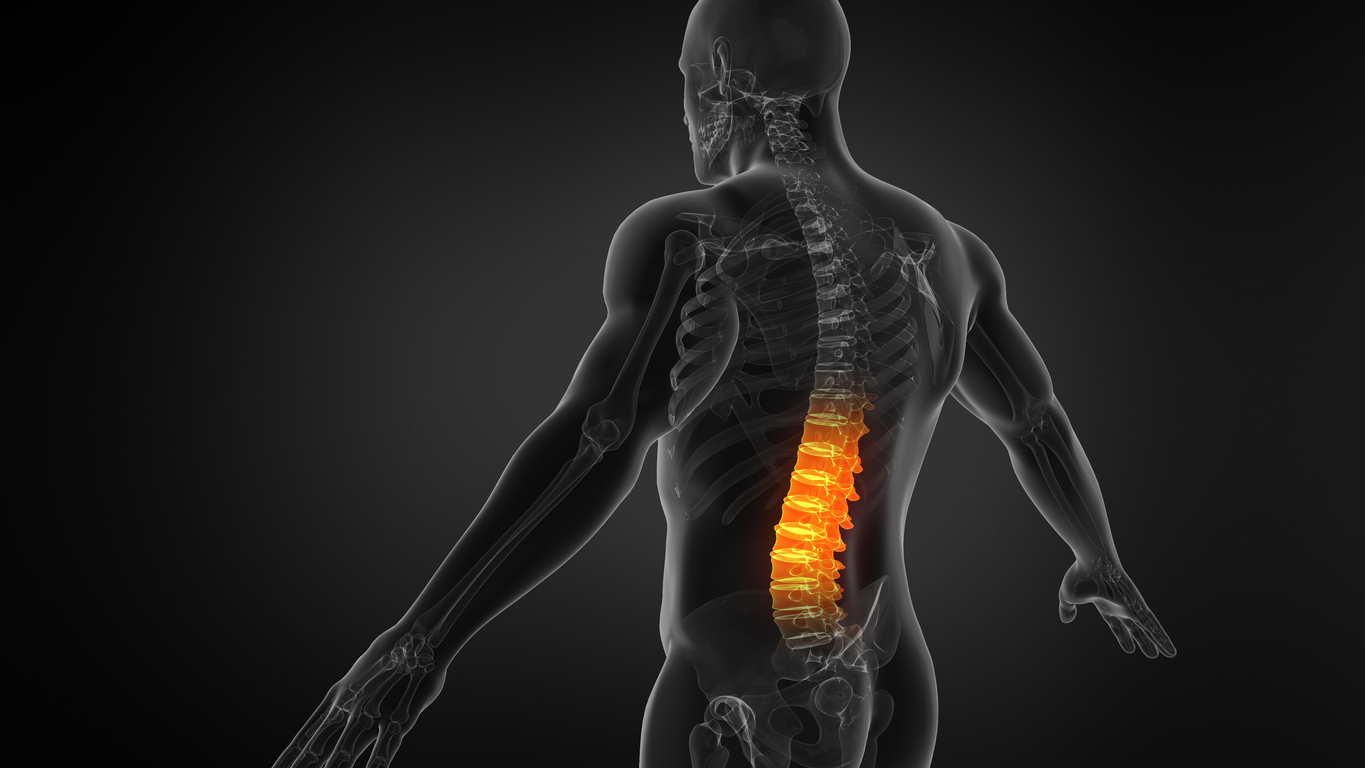
Adjacent segment disease (ASD) is a spinal condition that can develop after spinal surgery, especially after a spinal fusion. ASD involves degenerative changes that occur in an adjacent spinal segment to a surgically treated spinal segment. These degenerative changes cause radiculopathy, myelopathy, or spinal instability.
What causes ASD?
Most commonly, ASD is a complication of spinal fusion surgery. When two or more vertebrae are fused together, the segments above and below the fusion (the adjacent vertebrae) compensate for the loss of mobility in the fused segments. Because these vertebrae take on additional stress, they are at increased risk of disc degeneration, which can lead to pain above and below the fusion. If segments above and below fused segments already began to degenerate before surgery, the likelihood that adjacent segment disease will develop after spinal surgery increases.
What are the symptoms of ASD?
Adjacent segment disease often presents with symptoms similar to the symptoms that indicated the first spinal surgery was needed.
Adjacent segment disease that develops after a lumbar spine (low back) surgery may present with the following symptoms:
- Pain while walking
- Difficulty standing
- Low back pain
- Pain that radiates from the low back to the legs or feet
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the lower extremities
Adjacent segment disease that develops after a cervical spine (neck) surgery may present with the following symptoms:
- Neck pain
- Pain that radiates from the neck to the shoulders, arms, and/or hands
- Tingling, numbness, or weakness in the neck and/or upper extremities
Other symptoms of ASD are dependent on the specific degenerative changes to the spine and where they are located (cervical or lumbar spine). For example, additional symptoms of ASD associated with spinal osteoarthritis differ from symptoms ASD related to spinal stenosis.
Some cases of ASD are asymptomatic. These cases do not present with symptoms, but the condition may be detected on an MRI.
What are the risk factors for ASD?
Risk factors associated with adjacent segment disease include the following:
- Previous spinal fusion, particularly multi-level spinal fusion, fusion of the L4-L5 spinal segment, or traditional rather than minimally invasive spinal surgery
- Existing degenerative spinal disorder (e.g., herniated disc) prior to spinal fusion
- Advanced age
- Female
- Nicotine use
Additional source: HealthCentral