Pain
What Could Be Causing My Arm Pain?

Arm pain occurs when there is pain or discomfort anywhere along the arm, including the shoulder, elbow and wrist. It can be constant or intermittent, and develop suddenly or gradually. Arm pain ranges in severity from a slight inconvenience to a life-threatening alert. It can result from various different health conditions or injuries. If the origin of arm pain is unknown, a medical professional should be consulted for a proper diagnosis. In some cases, arm pain may originate in the upper spine or neck.
Seek immediate emergency medical assistance if arm pain resembles that of a heart attack, or if it is accompanied by chest pain, dizziness, nauseousness, or shortness of breath. Heart attack arm pain can occur in one or both arms.
Symptoms
Symptoms of arm pain vary, depending on the cause. Arm pain may begin in other areas of the body and radiate into the arm region to include the shoulder, neck, back, wrist, and surrounding nerves. Symptoms include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Swelling
- Pain, discomfort or tenderness
- Aching or sore
- Numbness or tingling
- Irritation
- Stiffness
- Limited range of motion
- Weakness
- Inflammation
- Bruising or redness
- Itching
- Swollen lymph nodes under the arm
Possible causes
The most common cause of arm pain is injury or overuse. Other possible causes include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Angina
- Brachial plexus injury
- Broken bone in the arm, wrist, hand or shoulder
- Bursitis
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Cervical disk herniation
- Daily activities, such as typing, writing, heavy lifting, sports, exercising, working with tools, etc.
- Deep vein thrombosis in the upper extremity
- Dislocated elbow
- De Quervain tenosynovitis
- Fibromyalgia
- Frozen Shoulder
- Heart attack
- Pinched nerve
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rotator cuff injury
- Sprains
- Tendinitis
- Thoracic outlet syndrome
- Ulnar nerve entrapment
Risk factors
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing arm pain. They include the following:
- Female
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Thyroid issues
- Pregnancy
- Repetitive movements
Diagnosing
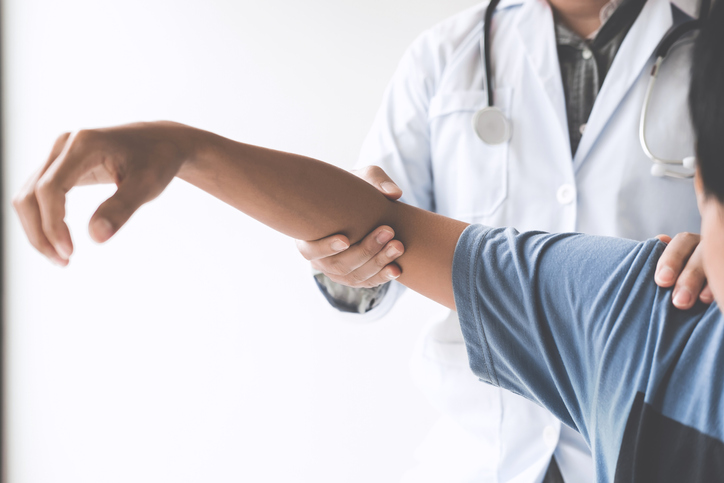
A health care professional will gather a medical history and perform a physical examination. Testing can include range of motion, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, CT scan, and blood test.
Treatment options
Treatment options for arm pain will vary depending on the cause. Common forms of treatment include prescribed pain or anti-inflammatory medication, injections and intravenous medications, or physical therapy. Surgery may be necessary in severe cases, such as a broken bone or torn ligament.
Home remedies may include resting the arm, compression, ice therapy, warm compression, or over-the-counter medications. Elevating the arm can reduce pain. It decreases the amount of blood flow to the nerves that send pain signals to the brain, resulting in a decreased perception of pain. Anti-inflammatory essential oils can also be massaged into the painful area.