Pain
Types of Psoriasis
Source: Mayo Clinic, WebMD, Healthline, National Center for Biotechnology Information: U.S. National Library of Medicine: National Institutes of Health, WebMD, Medscape, National Center for Biotechnology Information: U.S. National Library of Medicine: National Institutes of Health
1 person found this helpful
Print
Share
Save
What is psoriasis?
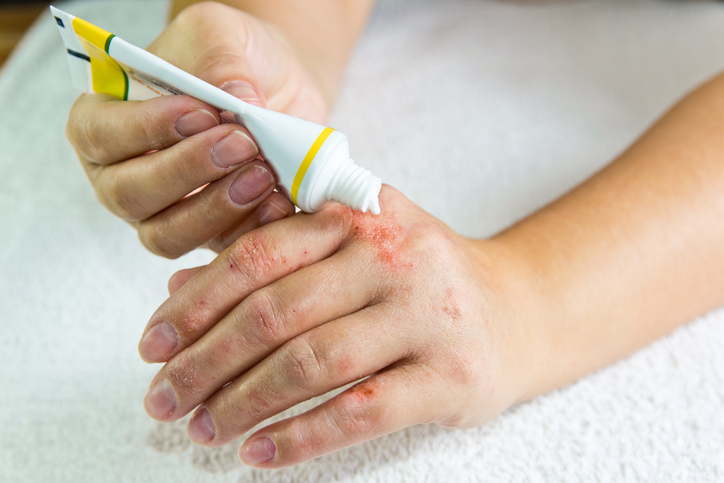
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that causes skin cells to multiply up to 10 times faster than normal. There is a wide spectrum of severity and manifestations of psoriasis, but common characteristics of most types of psoriasis include skin redness (erythema), thickening, and scaling (squamae).
Symptoms of psoriasis range from pinhead-sized spots on the skin to major eruptions that cover large areas of skin. Symptoms most commonly occur in cycles, flaring for a few weeks or months, then subsiding or going into remission; however, it may also be monophasic, meaning symptoms only occur once. It is possible to have more than one type of psoriasis.
Types of psoriasis
Types of psoriasis include the following:
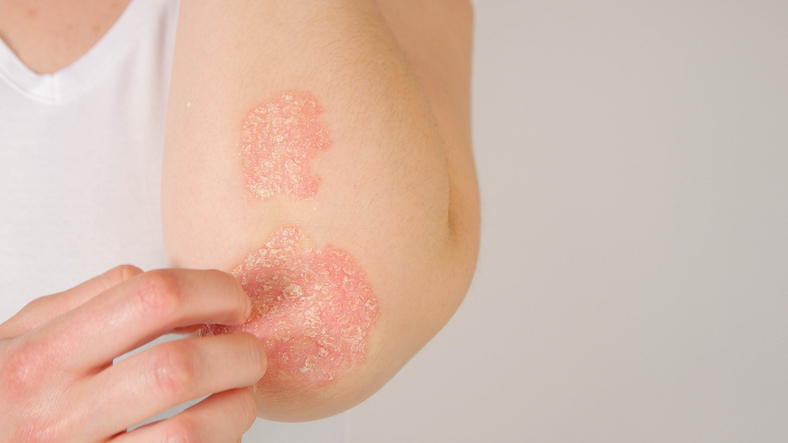
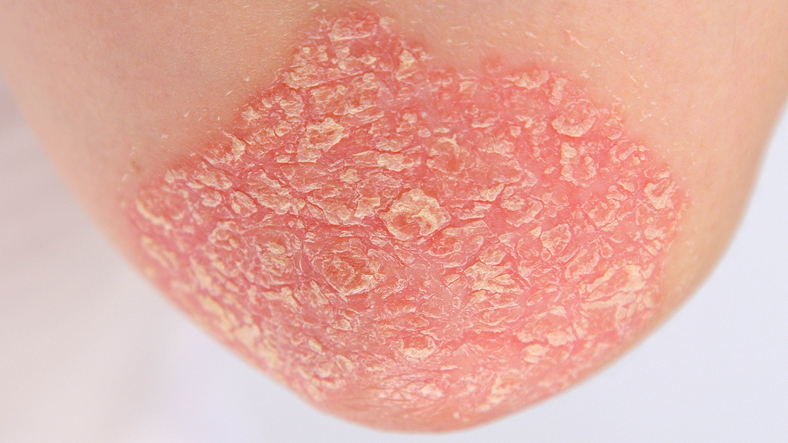
- Plaque psoriasis is the most common type of psoriasis and is characterized by raised, red skin lesions covered with silvery scales. These plaques may be tender or itchy. Symptoms commonly appear on the elbows, knees, lower back, and scalp.
- Nail psoriasis can affect both fingernails and toenails. Symptoms include nail discoloration, pitting, abnormal growth, or separation from the nail bed (onycholysis).
- Scalp psoriasis is common in individuals with plaque psoriasis. It is painful, itchy, very noticeable from the hairline, and can cause severe dandruff. It affects approximately 50% of individuals who have another type of psoriasis.
- Oral psoriasis develops in the mouth (most commonly the inside of the cheek) and is characterized by patches of red skin with white or yellow edges. Other symptoms include mouth sores, blisters filled with pus, peeling skin on the gums, pain or burning when eating spicy food, or a change in how things taste. Symptoms are often short-term and mild.
- Linear psoriasis is a rare presentation of psoriasis. Eruptions appear in linear lines that follow the lines of natural cell development in the skin (Blaschko’s lines). Plaques are not present anywhere else on the body. Linear psoriasis tends to develop later in life.
- Napkin psoriasis is a form of psoriasis that is most prevalent in children (typically 2 years of age or younger) who wear diapers. It is typically associated with other disorders that cause diaper rash.
- Guttate psoriasis primarily affects children and young adults. It is usually triggered by an infection such as strep throat. It is characterized by small, red, scattered, teardrop-shaped spots on the skin. It commonly presents on the trunk, arms or legs; however, it may also cover the entire body.
- Inverse psoriasis involves smooth patches of skin that worsen with friction and sweating. It is usually found in skin folds of the groin, buttocks and breasts.
- Pustular psoriasis is characterized by pus-filled lesions on the skin. Symptoms may be localized to small areas (such as the palms of the hands or soles of the feet) or generalized. Impetigo herpetiformis is a rare form of generalized pustular psoriasis that can develop during pregnancy.
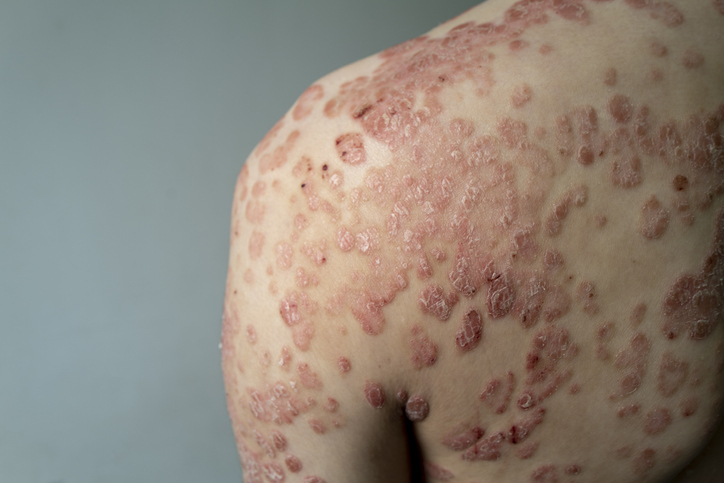
- Erythrodermic psoriasis is characterized by an extensive red, peeling rash that may cover the entire body. The rash may itch or burn.
- Psoriatic arthritis may be the first and only sign of psoriasis. It is characterized by typical arthritis symptoms: painful, swollen, stiff joints. Any joint can be affected. Severity ranges from mild to severe. In some cases, joint damage is permanent.