Pain
Types of Myositis
Source: Harvard Health, Healthline, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke: National Institutes of Health, Healthline
1 person found this helpful
Print
Share
Save
Myositis is the medical term used to describe a group of conditions that involve muscle inflammation. This inflammation can damage the fibers of the muscles, which prevents the muscles from contracting normally, causing muscle weakness. Depending on the cause, myositis can be acute (short-term), resolving in days or weeks, or it can be chronic (long-term).
Myositis is categorized into several types:
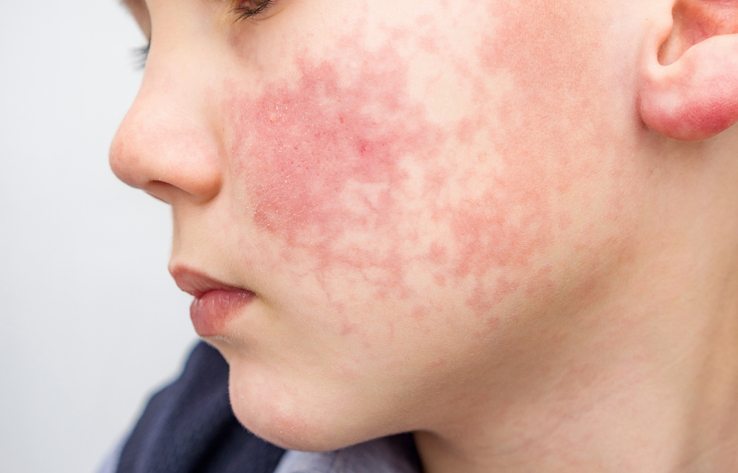
- Dermatomyositis starts with a purple/red rash on the face, chest, neck, back, and on the skin that covers the joints. The muscle weakness associated with myositis typically occurs after the rash appears. Dermatomyositis is thought to be an autoimmune condition.
- Polymyositis affects muscles on both sides of the body. It usually affects the muscles closest to the trunk of the body first and then spreads from there. Polymyositis is also thought to be an autoimmune condition. It tends to occur with other autoimmune diseases.
- Inclusion body myositis (IBM) starts by affecting muscles in the fingers, wrists, and thighs. It is often asymmetric, affecting one side of the body more than the other. IBM is thought to have a genetic component, so it can be passed from one generation to the next.
- Infectious myositis develops as a result of viral infections (e.g., the flu), bacterial infections, or parasitic infections.
- Toxic myositis (drug-induced myositis) is caused by substances, such as cholesterol-lowering medications, certain medications that suppress the immune system, cocaine, or other drugs. Symptoms are similar to other forms of myositis. This type of myositis can usually be reversed by eliminating use of the substance.
- Myositis ossificans (MO) involves bone or bone-like tissue that forms inside a muscle. This can occur after an injury that deeply bruises the muscle. It is most common in the thigh or upper arm. Pain and range of motion in the affected muscle usually worsen within one to two weeks after the initial injury.
- Juvenile myositis (JM) affects children under the age of 18. Its primary symptoms are muscle weakness and a purple/red rash on the eyelids or joints.













