Pain
Conventional Treatments for Osteoarthritis (OA)
What is osteoarthritis?
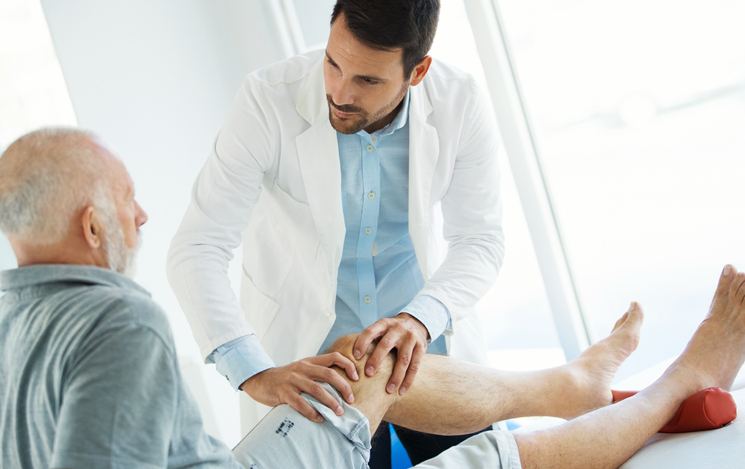
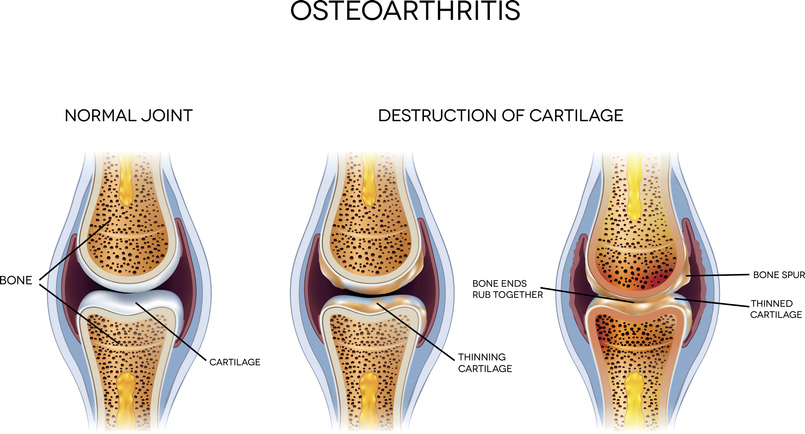
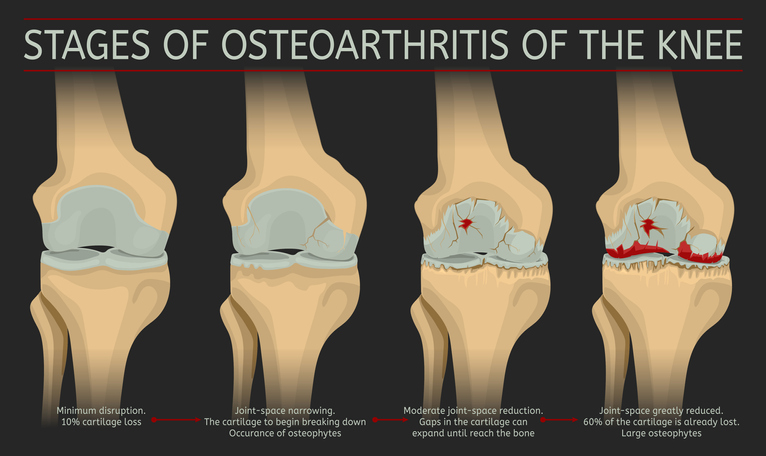
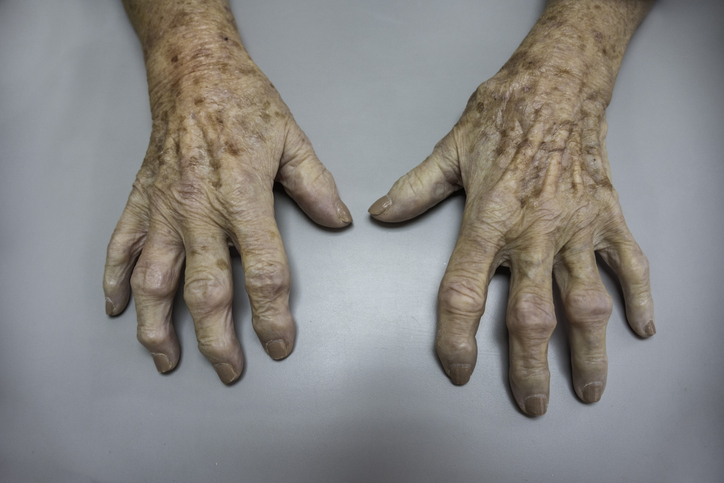
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, affecting over 30 million people in the United States alone. It occurs when the smooth cushion (cartilage) in one or more joints gradually breaks down, causing joint pain and stiffness. Osteoarthritis most commonly affects the hands, knees, hips and spine. Because OA is typically caused by normal wear and tear, the risk of developing osteoarthritis increases with age and generally worsens over time.
Treatments
While there is not a cure for osteoarthritis (OA), treatments can reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. Conventional treatments for OA include medications, physical therapy, injections and surgery.
Medications
Medications used to treat OA include the following:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDS)
NSAIDs help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. - Oral pain medications
Over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen, or prescription medications, such as opioids, can reduce pain. - Topical medications
Creams or gels containing menthol or capsaicin can be applied directly to the skin over painful joints. Gels that contain NSAIDs, such as diclofenac, are available by prescription. - Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are powerful prescription anti-inflammatories that can reduce joint swelling and pain. They can be taken orally or injected directly into the joint by a physician. - Duloxetine
Duloxetine is often used as an antidepressant, but it is also approved to treat chronic pain, including OA pain. - Pregabalin
Pregabalin is an anti-seizure medication that is also approved to treat OA pain.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles around the joint and improve flexibility, both of which can reduce pain.
Assistive devices
Braces, splints, shoe inserts, canes, or walkers are assistive devices that can provide support for weakened joints, reducing pain.
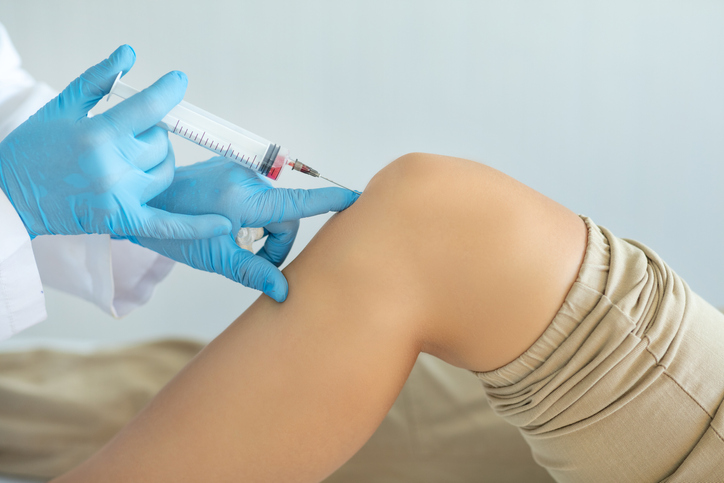
Hyaluronic acid injections
Hyaluronic acid is similar to the joint fluid naturally found in the body. When injected into a joint, it can provide some additional cushioning.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP)
Platelet-rich plasma contains proteins that may reduce both pain and inflammation. It is injected by a physician.
Surgery
If non-invasive treatment methods are not successful, surgery may be necessary. Surgical options for OA include the following:
- Bone realignment
Also known as osteotomy, this procedure involves realigning bones that have been damaged by arthritis in order to relieve stress on the bone or joint. This procedure is most useful when one side of the joint is more damaged than the other. - Bone fusion
Also known as arthrodesis, this procedure involves permanently fusing the bones in a joint together to increase stability and reduce pain. Since this significantly reduces or eliminates range of motion in a joint, it is typically only used in severe cases of OA. - Arthroscopic surgery
In this procedure, a surgeon uses a small camera known as an arthroscope to see inside a joint and remove torn or damaged cartilage or bone spurs. - Joint replacement
Also known as arthroplasty, this procedure involves removing the damaged joint and replacing it with a plastic or metal prosthetic.
Many treatment options are available to help relieve osteoarthritis symptoms, increase mobility, and improve quality of life.