Pain
Conventional Medical Treatments for Fibromyalgia

What is fibromyalgia?
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain syndrome that involves widespread muscle pain (myalgias) and joint pain (arthralgias). In addition to pain, fibromyalgia is frequently accompanied by additional symptoms, including fatigue, cognitive impairment/brain fog, headaches, depression, anxiety and insomnia.
The goal of fibromyalgia treatment is to reduce pain and symptoms of the condition to improve quality of life. Fibromyalgia is often managed using a combination of medications and physical therapy.
Medications
Most medications prescribed for fibromyalgia address the primary symptom of pain. Types of pain medication used to treat fibromyalgia pain include analgesics, antidepressants, and anti-seizure medications.
- Analgesics, such as ibuprofen, naproxen sodium, acetaminophen, or opioids, can help manage pain.
- Antidepressants can help ease fibromyalgia pain even when coexisting depression is not an issue. Types of antidepressants often prescribed for fibromyalgia pain include serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), such as duloxetine and milnacipran; selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), including fluoxetine and sertraline; and tricyclics, such as amitriptyline.
- Anti-seizure medications, such as pregabalin and gabapentin, may also be prescribed to ease fibromyalgia pain.
Additionally, any of the following medications may be prescribed to manage fatigue and sleep issues:
- Stimulants, such as modafinil and dextroamphetamine-amphetamine
- Sedatives, such as zolpidem or diazepam
- Muscle relaxers, such as cyclobenzaprine
- Melatonin (a supplement that may help improve both sleep patterns and pain)
Physical therapy
Physical therapy can also help manage fibromyalgia pain and fatigue. The goal of physical therapy is to develop, improve and maintain maximum body function and movement. Physical therapists can provide individualized stretching and strengthening regimens. In addition to stretching and strengthening exercises, physical therapists may recommend the following therapies:
- Deep tissue massage
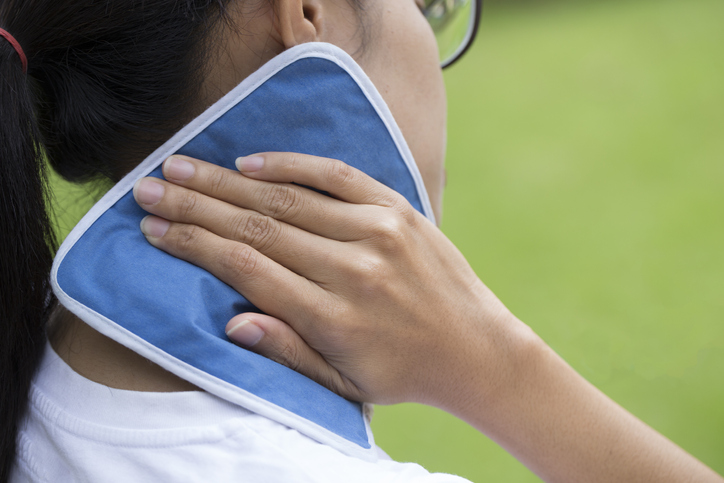
- Temperature therapy, such as cold compresses and moist heat
- Low-impact aerobic conditioning (water therapy)
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)
- Therapeutic ultrasound
A physical therapist can also document an individual’s progress, ensure that the fibromyalgia-specific treatment program is properly implemented, and confirm that treatment goals are reached.