Pain
AAK1 Inhibitors as an Emerging Treatment for Neuropathic Pain

What is neuropathic pain?
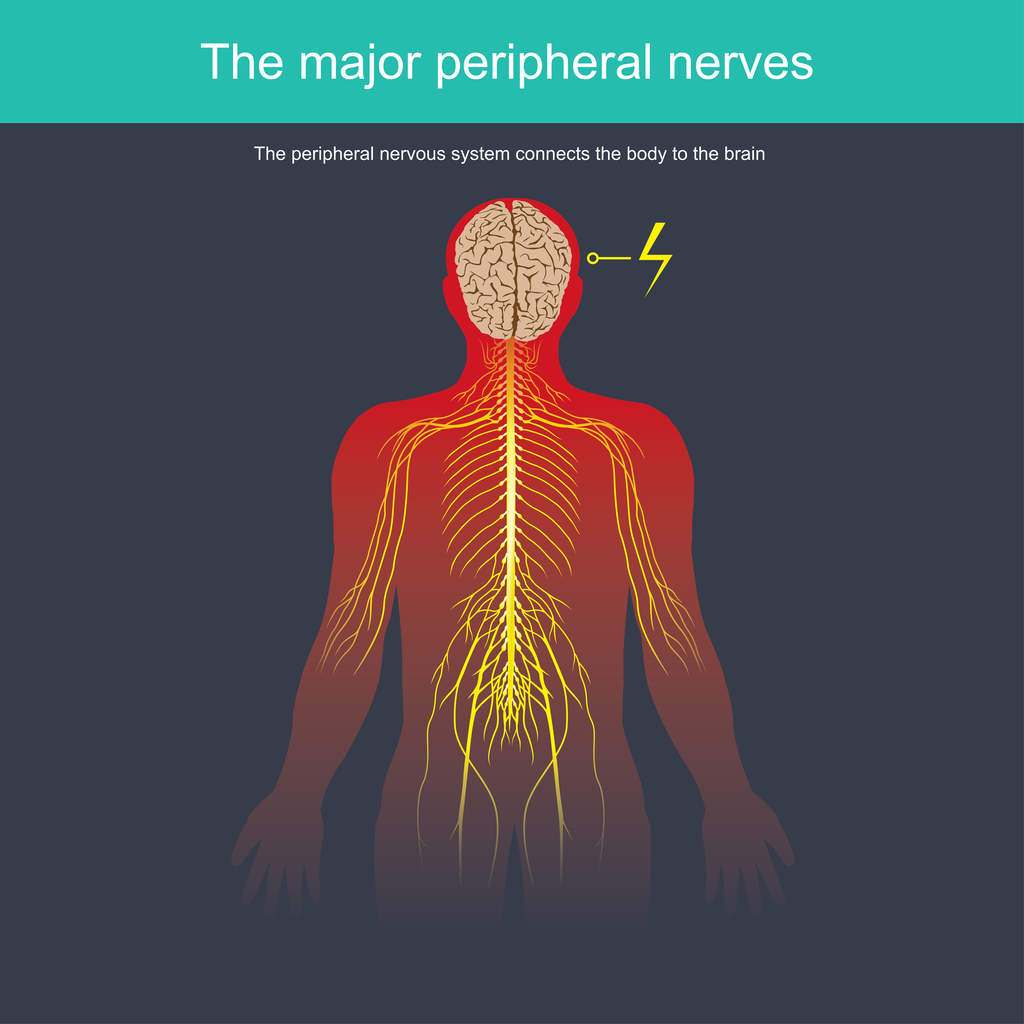
Neuropathic pain is a chronic pain condition that occurs due to nerve damage or a malfunctioning nervous system. The nervous system includes peripheral nerves, the brain, and the spinal cord. The central nervous system (CNS) includes the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral nerves spread throughout the body and transfer information between the brain and spinal cord from other parts of the body. Nerve damage can change the nerve function at an injury site or the area surrounding an injury, causing them to send wrong signals to pain centers.
AAK1 inhibitors
The adaptor-associated kinase 1 (AAK1) enzyme is primarily found in the brain and heart. This enzyme allows for chemical signals to be sent between cells in the body. AAK1 inhibitors interfere with this process. Though scientists do not yet know the exact reason, AAK1 inhibitors may reduce neuropathic pain.
Studies
Studies involving mice found that AAK1 inhibitors had similar pain relief to gabapentin, which is a medication often prescribed to treat neuropathic pain. AAK1 inhibitors appear to impact the central nervous system to reduce pain.
Initial studies involving humans found that AAK1 is generally well-tolerated. Most participants experienced only mild side effects, such as headaches, dizziness and nausea. Phase two and three trials are needed to determine overall safety and effectiveness of this treatment.
Conclusion
With additional research, AAK1 inhibitors may be found to be a viable treatment option for individuals with neuropathic pain who do not respond well to other available treatments.